7 Simple Techniques For Exercise Physiology - Exercise Science CUC - Concordia


Exercise Physiology Lab : Department of Health and Human Performance : Texas State University
Facts About Exercise Physiology, Ph.D< University of Oklahoma Uncovered
A male marathon runner loses each hour around 0. 83 L in cool weather and 1. 2 L in warm (losses in females have to do with 68 to 73% lower). Individuals doing heavy workout might lose 2 and half times as much fluid in sweat as urine. This can have profound physiological effects.
These impacts are mainly removed by changing 50 to 80% of the fluid lost in sweat. Plasma catecholamine concentrations increase 10-fold in entire body exercise. Ammonia is produced by exercised skeletal muscles from ADP (the precursor of ATP) by purine nucleotide deamination and amino acid catabolism of myofibrils. interleukin-6 (IL-6) increases in blood flow due to its release from working skeletal muscles.

Introduction to Exercise Physiology: 9781449698188: Medicine & Health Science Books @ Amazon.com
An Unbiased View of Exercise Physiology Major - Ohio Northern University

Salt absorption is affected by the release of interleukin-6 as this can cause the secretion of arginine vasopressin which, in turn, can result in exercise-associated dangerously low sodium levels (hyponatremia). This loss of salt in blood plasma can lead to swelling of the brain. This can be avoided by awareness of the threat of drinking excessive quantities of fluids throughout extended exercise.
The brain is normally dependent for its high energy expense upon aerobic metabolism. The brain as an outcome is extremely conscious failure of its oxygen supply with loss of consciousness occurring within six to seven seconds, with its EEG going flat in 23 seconds. Therefore, the brain's function would be interrupted if workout impacted its supply of oxygen and glucose.
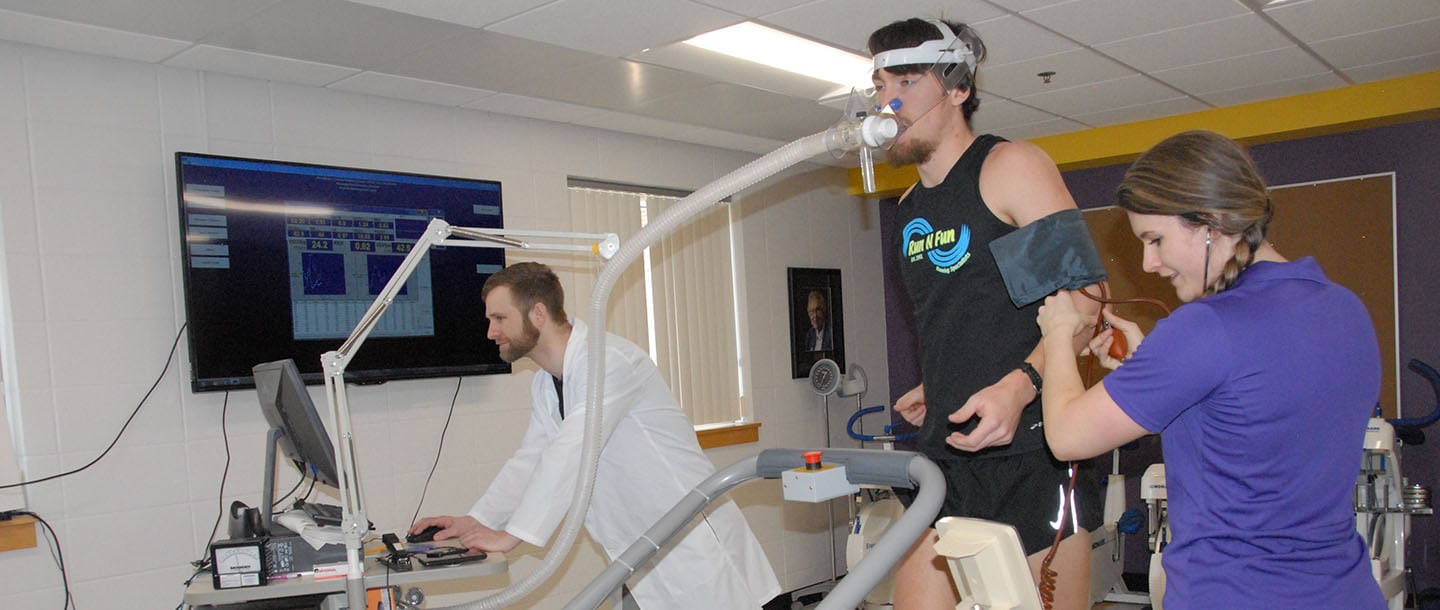
PhD in Exercise Physiology - School of Education - University of Pittsburgh
Examine This Report on Exercise Physiology - UK College of Education
Because humans are bipeds, motor control is needed for keeping balance. For this reason, brain energy intake is increased throughout extreme workout due to the needs in the motor cognition required to control the body. Exercise Physiologists treat a variety of neurological conditions including (but not restricted to): Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, Distressing Brain Injury, Back Cord Injury, Spastic paralysis and psychological health conditions.
During submaximal workout, heart output boosts and cerebral blood flow increases beyond the brain's oxygen requirements. However, This Is Noteworthy is not the case for continuous optimum exertion: "Optimum workout is, despite the boost in capillary oxygenation [in the brain], associated with a reduced mitochondrial O2 material during whole body exercise" The autoregulation of the brain's blood supply is impaired especially in warm environments Glucose [edit] In adults, exercise depletes the plasma glucose available to the brain: short extreme exercise (35 min ergometer biking) can reduce brain glucose uptake by 32%.
